
We introduce a de novo sequencing method of protein N terminus utilizing matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) signal enhancing picolinamidination with bromine isotopic tag incorporated to the N terminus. Conclusions: Mongolian HCC has unique molecular traits with a high mutational burden and a novel mutational signature associated with genotoxic environmental factors present in this country. De novo analysis of protein N-terminal sequence is important for identification of N-terminal proteolytic processing such as N-terminal methionine or signal peptide removal, or for the genome annotation of uncharacterized proteins. Transcriptomic-based analysis delineated two molecular clusters, one with a highly inflamed profile, not present in Western HCC, and that were significantly associated with HBV-HDV etiology and female gender.
This signature showed a distinct substitution profile with a high proportion of T>G substitutions and was significantly associated with exposure to the environmental agent dimethyl sulfate (DMS, 71%), a 2A carcinogenic associated with coal combustion. Four mutational signatures characterized Mongolian samples, one of which was novel (SBS Mongolia) and present in 25% of Mongolian HCC cases.
#De novo protein sequence analysis driver
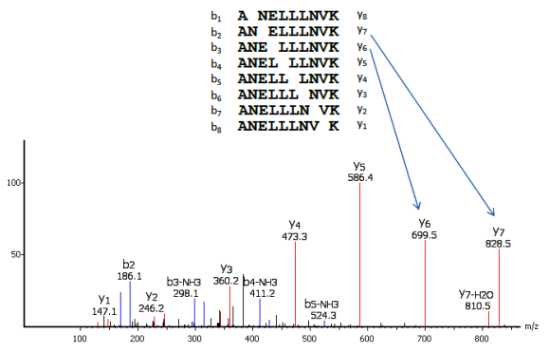
Mongolian HCCs presented significantly higher rates of protein-coding mutations (121 vs 70 mutations per tumor in Western), and in specific driver HCC genes (i.e. The other approach to identify peptides by tandem mass spectrometry is to match the fragment ions with virtual peptide. The concepts behind a number of de novo sequencing methods are discussed. Results: Mongolian patients were younger, with higher female prevalence, and with predominantly HBV-HDV co-infection etiology. In this study, two cellulose synthase genes, AmCesA1 and AmCesA2, were cloned from Acacia mangium using transcriptome de novo sequencing analysis and RACE. De novo sequencing is a method to analyze and identify peptide sequences and some post-translational modified proteins. De novo methods utilize computational approaches to deduce the sequence or partial sequence of peptides directly from the experimental MS/MS spectra. Both totalscore and rms are provided in the score file. To see how confident you can be about the correctness of a prediction, you can plot score vs. Experimental Design: We performed a molecular characterization of Mongolian (n=192) compared to Western HCCs (n=187) by RNA-seq and WES to unveil distinct genomic and transcriptomic features associated with environmental factors in this population. For de novo structure prediction, in general you will want to perform the following steps: 3.1.

Purpose: Mongolia has the world’s highest incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with ~100 cases/10 5 inhabitants, although the reasons for this feature have not been thoroughly delineated. Following mass spectrometric analysis, the (ppm), PEAKS and SPIDER score for confidence interval most abundant peptides in the mixture led to the most () for the PEAKS de novo generated peptide sequences accurate protein identification hence, less abundant and their corresponding homology searches.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
